About The Project
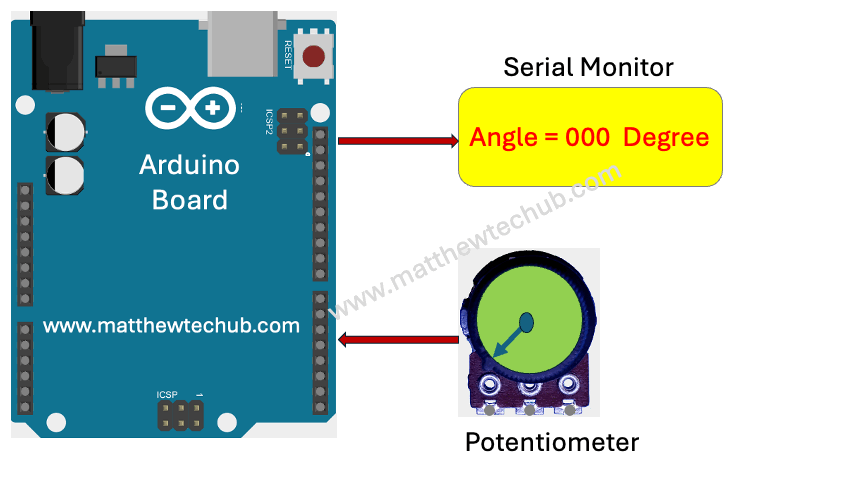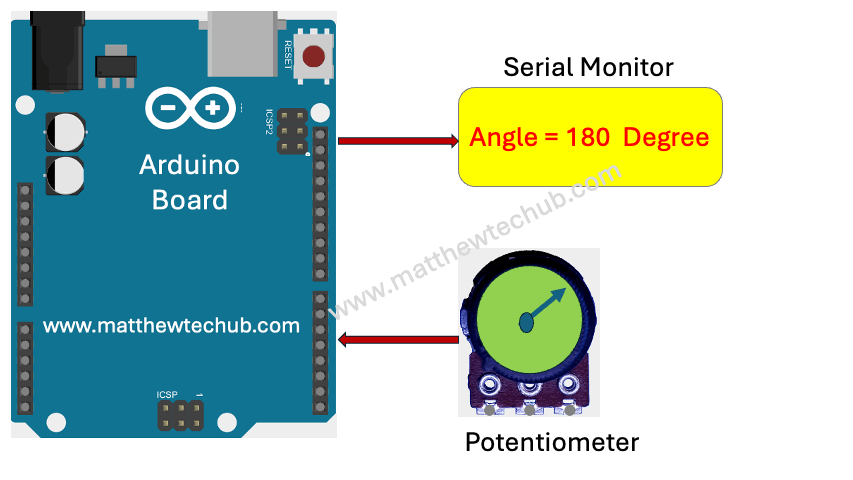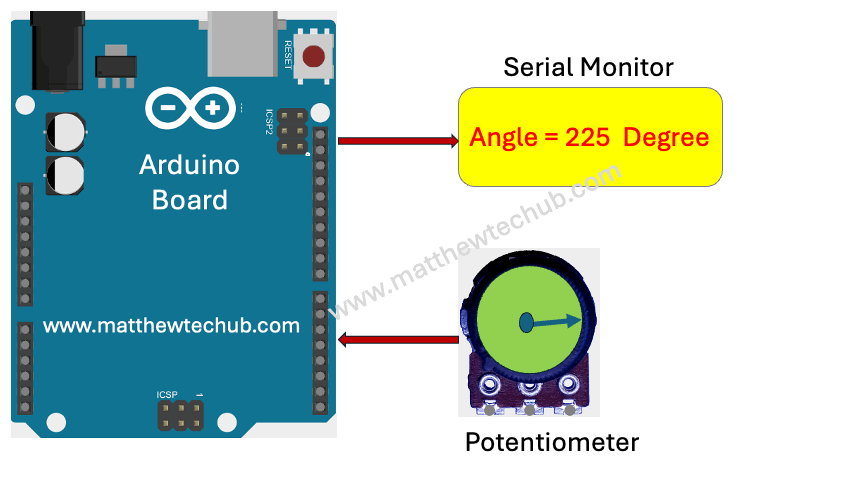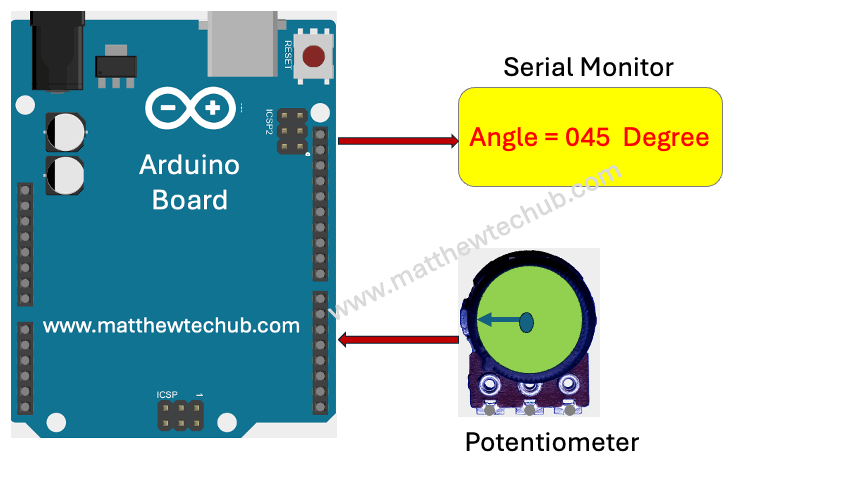
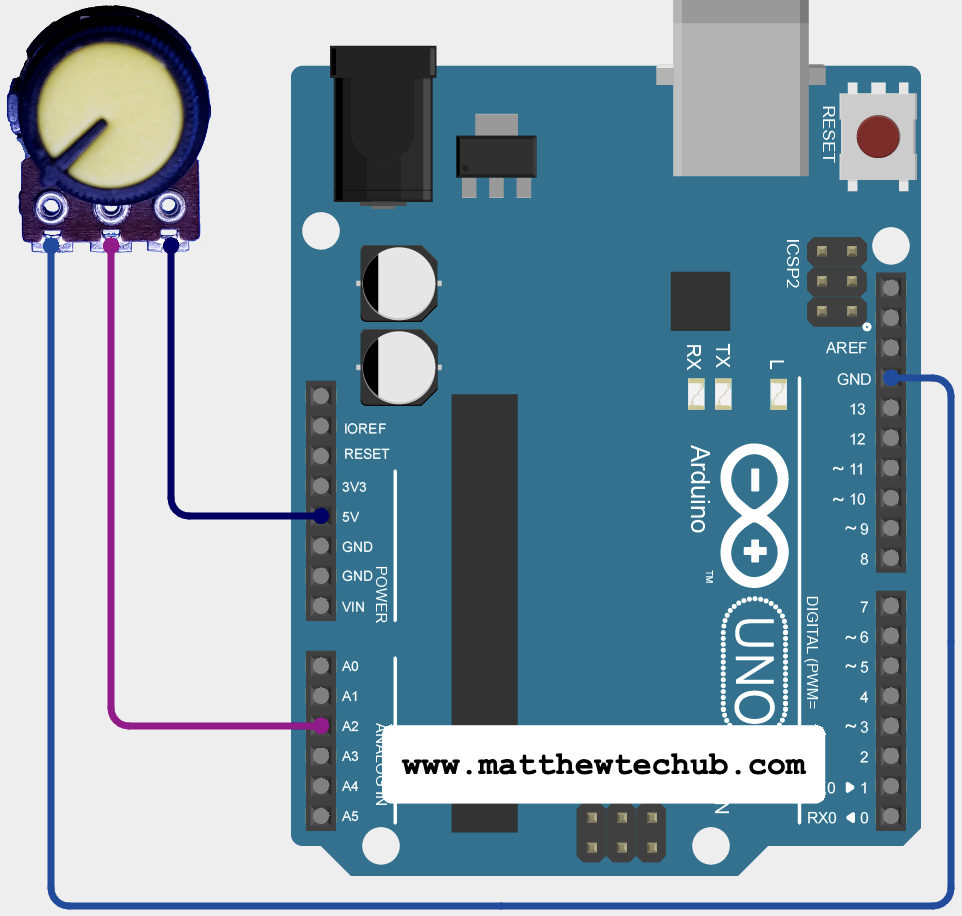
This project uses a potentiometer to measure angular displacement, ranging from 0 degrees to 270 degrees. The potentiometer’s analog output is read by an Arduino board using the analogRead() function, which provides values between 0 and 1023 corresponding to the potentiometer’s position. These analog values are converted into angular measurements using a linear mapping. The calculated angle is then displayed on the serial monitor connected to the Arduino, providing real-time feedback of the potentiometer’s angular position
Potentiometer
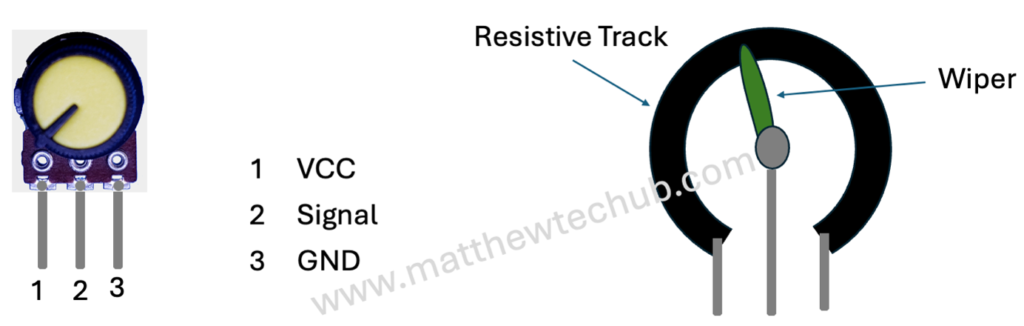
A rotary potentiometer or a pot, is an electromechanical component used to measure angular displacement or rotation. It consists of three terminals:
- Terminal 1 (GND): Connected to ground (0V).
- Terminal 2 (Wiper): The output terminal that moves along a resistive track inside the potentiometer as it is rotated.
- Terminal 3 (Vcc): Connected to a voltage source (typically 5V or 3.3V).
How it Works:
- Resistance Variation: Inside the potentiometer, there is a resistive element (often a carbon track) with a movable contact (wiper). When you rotate the shaft of the potentiometer, the wiper moves along this resistive track.
- Variable Voltage Divider: The potentiometer operates as a variable voltage divider:
- Terminal 1 (GND) and Terminal 3 (Vcc) are connected to provide a constant voltage across the resistive track.
- The voltage output (signal) at Terminal 2 (Wiper) varies linearly with the angular position of the potentiometer’s shaft relative to its terminals.
- Output Range: The output voltage at Terminal 2 (Wiper) typically varies from 0V to the supply voltage (5V).
Circuit Wiring
Programme Code
// www.matthewtechub.com
// angle measurement from 0 t0 270
const int midPin = 2; // Pin connected to the potentiometer
int value; // Variable to store the analog reading
float angle; // Variable to store the calculated angle
void setup() {
pinMode(midPin, INPUT);
Serial.begin(9600);
}
void loop() {
// Read the analog value from the potentiometer
value = analogRead(midPin);
// Map the analog value (0-1023) to the angle (0-270 degrees)
angle = (float)value * 270.0 / 1023.0;
// Print the analog value and calculated angle to the serial monitor
Serial.print("Analog value: ");
Serial.println(value);
Serial.print("Angle (degrees): ");
Serial.println(angle);
delay(1000); // Delay for stability and readability
}Code Explanation
const int midPin = 2; // Pin connected to the potentiometer
int value; // Variable to store the analog reading
float angle; // Variable to store the calculated angle
- midPin: Defines the Arduino pin number to which the potentiometer is connected (in this case, pin A2).
- value: Integer variable to store the analog reading obtained from the potentiometer.
- angle: Float variable to store the calculated angle based on the analog reading.
void setup() {
pinMode(midPin, INPUT); // Configures midPin as an input pin
Serial.begin(9600); // Initializes serial communication with baud rate 9600
}
- pinMode(midPin, INPUT);: Configures pin midPin (pin A2) as an input, indicating it will read data from the potentiometer.
- Serial.begin(9600);: Initialises serial communication at a baud rate of 9600 bits per second, enabling communication between the Arduino and a connected computer via the Serial Monitor
void loop() {
value = analogRead(midPin); // Read analog value from potentiometer
angle = (float)value * 270.0 / 1023.0; // Map analog value to angle range (0-270 degrees)
Serial.print(“Analog value: “); // Print label for analog value
Serial.println(value); // Print analog value read from potentiometer
Serial.print(“Angle (degrees): “); // Print label for calculated angle Serial.println(angle); // Print calculated angle in degrees
delay(1000); // Delay for 1 second (1000 milliseconds)
}
- analogRead(midPin);: Reads the analog voltage value from the potentiometer connected to midPin and assigns it to the variable value.
- Mapping to Angle (angle = (float)value * 270.0 / 1023.0;):
- Converts the analog value (value) from the range 0-1023 (output of analogRead()) to an angle in degrees (0-270).
- Uses floating-point arithmetic (float) to preserve decimal precision during the calculation.
- Serial Output (Serial.print() and Serial.println()):
- Outputs information to the Serial Monitor for debugging and monitoring:
- Prints the label “Analog value: ” followed by the actual analog reading from value.
- Prints the label “Angle (degrees): ” followed by the calculated angle from angle.
- delay(1000);: Introduces a delay of 1000 milliseconds (1 second) between each loop iteration. This delay stabilizes the output and prevents rapid updates on the Serial Monitor.